注意
跳转至底部 下载完整的示例代码。
plot_optimization_history
- optuna.visualization.matplotlib.plot_optimization_history(study, *, target=None, target_name='Objective Value', error_bar=False)[源代码]
使用 Matplotlib 绘制 study 中所有 trial 的优化历史记录。
另请参阅
- 参数:
- 返回:
一个
matplotlib.axes.Axes对象。- 返回类型:
注意
于 v2.2.0 添加为实验性功能。接口可能在未来版本中更改,恕不另行通知。请参阅 https://github.com/optuna/optuna/releases/tag/v2.2.0。
以下代码片段展示了如何绘制优化历史记录。
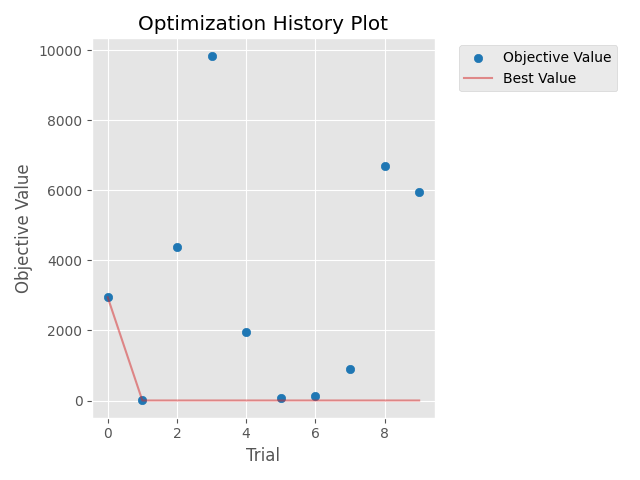
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/optuna/checkouts/stable/docs/visualization_matplotlib_examples/optuna.visualization.matplotlib.optimization_history.py:24: ExperimentalWarning:
optuna.visualization.matplotlib._optimization_history.plot_optimization_history is experimental (supported from v2.2.0). The interface can change in the future.
<Axes: title={'center': 'Optimization History Plot'}, xlabel='Trial', ylabel='Objective Value'>
import optuna
def objective(trial):
x = trial.suggest_float("x", -100, 100)
y = trial.suggest_categorical("y", [-1, 0, 1])
return x**2 + y
sampler = optuna.samplers.TPESampler(seed=10)
study = optuna.create_study(sampler=sampler)
study.optimize(objective, n_trials=10)
optuna.visualization.matplotlib.plot_optimization_history(study)
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.289 秒)