注意
转到底部 下载完整的示例代码。
plot_edf
- optuna.visualization.matplotlib.plot_edf(study, *, target=None, target_name='Objective Value')[源代码]
使用 Matplotlib 绘制研究的目标值 EDF(经验分布函数)。
请注意,绘制 EDF 时仅考虑已完成的 trial。
另请参阅
有关示例,请参阅
optuna.visualization.plot_edf(),其中此函数可以替换它。注意
请参阅 matplotlib.pyplot.legend 来调整生成图例的样式。
- 参数:
- 返回:
一个
matplotlib.axes.Axes对象。- 返回类型:
注意
于 v2.2.0 添加为实验性功能。接口可能在未来版本中更改,恕不另行通知。请参阅 https://github.com/optuna/optuna/releases/tag/v2.2.0。
以下代码片段显示了如何绘制 EDF。
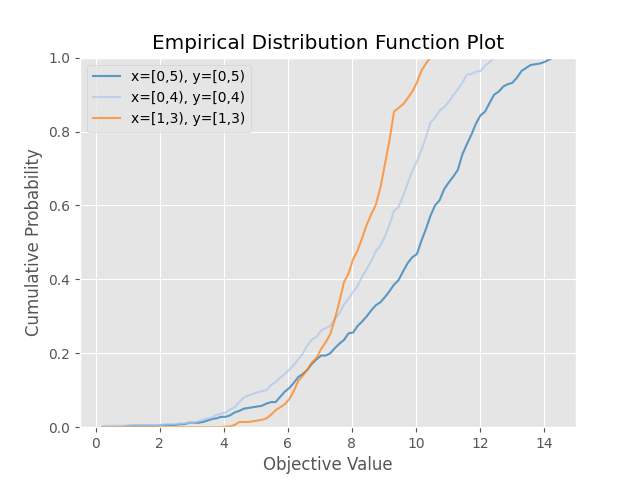
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/optuna/checkouts/stable/docs/visualization_matplotlib_examples/optuna.visualization.matplotlib.edf.py:43: ExperimentalWarning:
optuna.visualization.matplotlib._edf.plot_edf is experimental (supported from v2.2.0). The interface can change in the future.
<Axes: title={'center': 'Empirical Distribution Function Plot'}, xlabel='Objective Value', ylabel='Cumulative Probability'>
import math
import optuna
def ackley(x, y):
a = 20 * math.exp(-0.2 * math.sqrt(0.5 * (x**2 + y**2)))
b = math.exp(0.5 * (math.cos(2 * math.pi * x) + math.cos(2 * math.pi * y)))
return -a - b + math.e + 20
def objective(trial, low, high):
x = trial.suggest_float("x", low, high)
y = trial.suggest_float("y", low, high)
return ackley(x, y)
sampler = optuna.samplers.RandomSampler(seed=10)
# Widest search space.
study0 = optuna.create_study(study_name="x=[0,5), y=[0,5)", sampler=sampler)
study0.optimize(lambda t: objective(t, 0, 5), n_trials=500)
# Narrower search space.
study1 = optuna.create_study(study_name="x=[0,4), y=[0,4)", sampler=sampler)
study1.optimize(lambda t: objective(t, 0, 4), n_trials=500)
# Narrowest search space but it doesn't include the global optimum point.
study2 = optuna.create_study(study_name="x=[1,3), y=[1,3)", sampler=sampler)
study2.optimize(lambda t: objective(t, 1, 3), n_trials=500)
optuna.visualization.matplotlib.plot_edf([study0, study1, study2])
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 0.618 秒)